MUSE specific tools (mpdaf.MUSE)¶
Python interface for MUSE slicer numbering scheme¶
The Slicer class contains a set of static methods to convert
a slice number between the various numbering schemes. The definition of the
various numbering schemes and the conversion table can be found in the “Global
Positioning System” document (VLT-TRE-MUSE-14670-0657).
All the methods are static and thus there is no need to instantiate an object to use this class.
For example, we convert slice number 4 in CCD numbering to SKY numbering:
In [1]: from mpdaf.MUSE import Slicer
In [2]: Slicer.ccd2sky(4)
Out[2]: 10
Now we convert slice number 12 of stack 3 in OPTICAL numbering to CCD numbering:
In [3]: Slicer.optical2sky((2, 12))
Out[3]: 25
MUSE LSF models¶
Warning
LSF class is currently under development
Only one model of LSF (Line Spread Function) is currently available.
LSF qsim_v1¶
This is a simple model where the LSF is supposed to be constant over the filed of view. It uses a simple parametric model of variation with wavelength.
The model is a convolution of a step function with a Gaussian. The resulting function is then sample by the pixel size:
LSF = T(y2+dy/2) - T(y2-dy/2) - T(y1+dy/2) + T(y1-dy/2)
T(x) = exp(-x**2/2) + sqrt(2*pi)*x*erf(x/sqrt(2))/2
y1 = (y-h/2) / sigma
y2 = (y+h/2) / sigma
The slit width is assumed to be constant (h = 2.09 pixels). The Gaussian sigma parameter is a polynomial approximation of order 3 with wavelength:
c = [-0.09876662, 0.44410609, -0.03166038, 0.46285363]
sigma(x) = c[3] + c[2]*x + c[1]*x**2 + c[0]*x**3
To use it, create a LSF object with attribute ‘typ’ equal to
‘qsim_v1’:
In [4]: from mpdaf.MUSE import LSF
In [5]: lsf = LSF(typ='qsim_v1')
Then get the LSF array by using get_LSF:
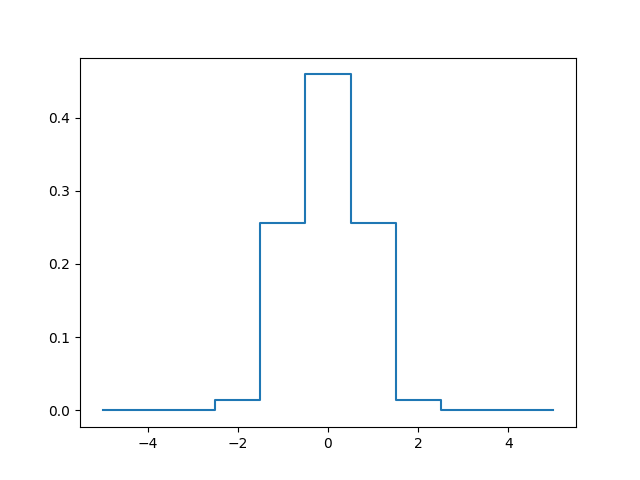
In [6]: lsf_6000 = lsf.get_LSF(lbda=6000, step=1.25, size=11)
In [7]: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
In [8]: import numpy as np
In [9]: plt.plot(np.arange(-5,6), lsf_6000, drawstyle='steps-mid')
Out[9]: [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f78462e8d68>]
MUSE FSF models¶
Warning
FSF class is currently under development
Two models of FSF (Field Spread Function) are currently available:
OldMoffatModel(model='MOFFAT1'): the old model with a fixed beta.MoffatModel2(model=2): a circular MOFFAT with polynomials for beta and FWHM.
Example with MOFFAT1¶
The MUSE FSF is supposed to be a Moffat function with a FWHM which varies linearly with the wavelength:
\(FWHM = a + b * lbda\)
With:
- beta (float) Power index of the Moffat.
- a (float) constant in arcsec which defined the FWHM.
- b (float) constant which defined the FWHM.
We create the FSFModel object like this:
In [10]: from mpdaf.MUSE import FSFModel, OldMoffatModel
In [11]: fsf = OldMoffatModel(a=0.885, b=-2.94E-05, beta=2.8, pixstep=0.2)
In [12]: isinstance(fsf, FSFModel)
Out[12]: True
Various methods allow to get the FSF array (2D or 3D, as mpdaf Image or Cube) for given wavelengths, or the FWHM in pixel and in arcseconds.
In [13]: lbda = np.array([5000, 9000])
In [14]: fsf.get_fwhm(lbda)
Out[14]: array([0.738 , 0.6204])
In [15]: fsf.get_fwhm(lbda, unit='pix')
���������������������������������Out[15]: array([3.69 , 3.102])
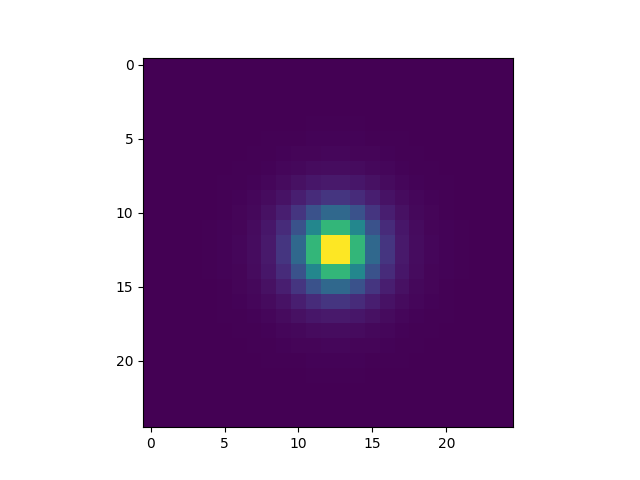
In [16]: im5000 = fsf.get_2darray(lbda[0], shape=(25, 25))
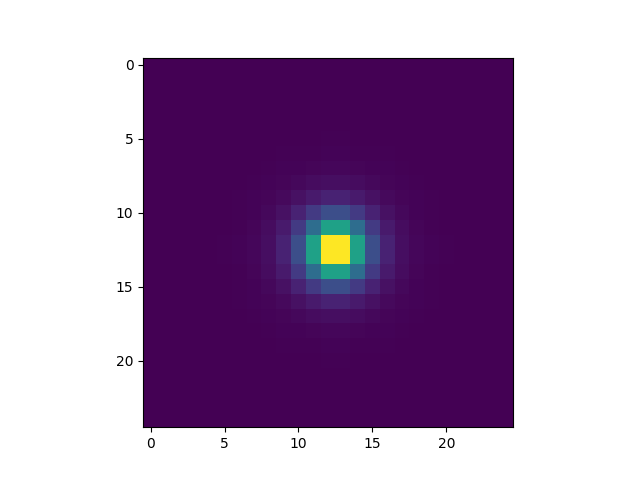
In [17]: fsfcube = fsf.get_3darray(lbda, shape=(25, 25))
In [18]: plt.figure()
Out[18]: <Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes>
In [19]: plt.imshow(im5000)
�������������������������������������������Out[19]: <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f7851691d30>
In [20]: plt.figure()
Out[20]: <Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes>
In [21]: plt.imshow(fsfcube[1])
�������������������������������������������Out[21]: <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f78511f2588>
The FSF model can be saved to a FITS header with
mpdaf.MUSE.FSFModel.to_header, and read with mpdaf.MUSE.FSFModel.read.
MUSE mosaic field map¶
Warning
FieldsMap class is currently under development
FieldsMap reads the possible FIELDMAP extension of the MUSE data
cube.
In [22]: from mpdaf.MUSE import FieldsMap
In [23]: fmap = FieldsMap('sdetect/subcub_mosaic.fits', extname='FIELDMAP')
get_pixel_fields returns a list of fields that cover
a given pixel (y, x):
In [24]: fmap.get_pixel_fields(0,0)
Out[24]: ['UDF-06', 'UDF-09']
In [25]: fmap.get_pixel_fields(20,20)
������������������������������Out[25]: ['UDF-06']
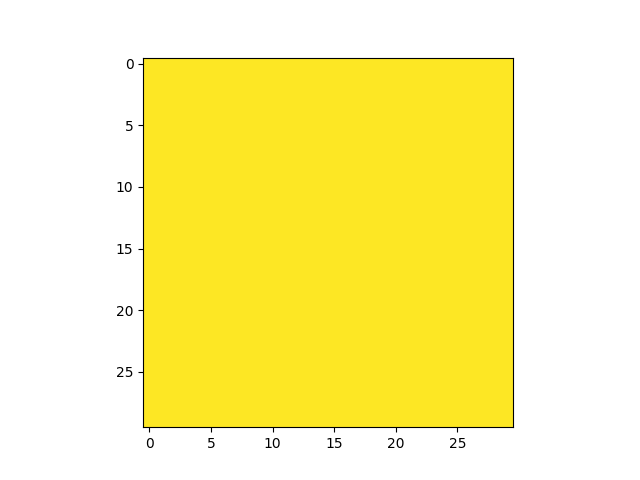
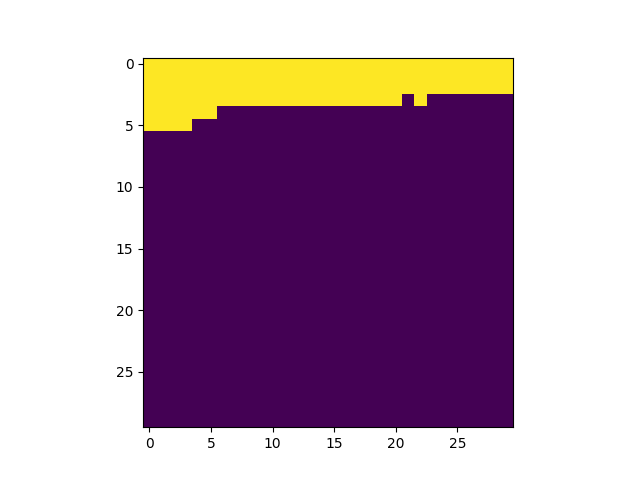
get_field_mask returns an array with non-zeros values
for pixels matching a field:
In [26]: plt.figure()
Out[26]: <Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes>
In [27]: plt.imshow(fmap.get_field_mask('UDF-06'), vmin=0, vmax=1)
�������������������������������������������Out[27]: <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f78514aca58>
In [28]: plt.figure()
Out[28]: <Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes>
In [29]: plt.imshow(fmap.get_field_mask('UDF-09'), vmin=0, vmax=1)
�������������������������������������������Out[29]: <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f78514c8cc0>
Reference/API¶
mpdaf.MUSE Package¶
Functions¶
FSF([typ]) |
This class offers Field Spread Function (FSF) models for MUSE. |
Moffat2D(fwhm, beta, shape[, center, normalize]) |
Compute Moffat for a value or array of values of FWHM and beta. |
create_psf_cube(shape, fwhm[, beta, wcs, …]) |
Create a PSF cube with FWHM varying along each wavelength plane. |
get_FSF_from_cube_keywords(cube, size) |
Return a cube of FSFs corresponding to the keywords presents in the MUSE data cube primary header (‘FSF***’) |
Classes¶
FSFModel() |
Base class for FSF models. |
FieldsMap([filename, nfields]) |
Class to work with the mosaic field map. |
LSF([typ]) |
This class offers Line Spread Function models for MUSE. |
MoffatModel2(fwhm_pol, beta_pol, lbrange, …) |
|
OldMoffatModel(a, b, beta, pixstep[, field]) |
Moffat FSF with fixed beta and FWHM varying with wavelength. |
Slicer |
Convert slice number between the various numbering schemes. |